Nov 21 2013
An international team of researchers has synthesized a new material that stores an unusually large amount of hydrogen. Performing high-pressure X-ray studies at DESY's PETRA III and other light sources, the scientists detected the formation of previously unobserved iridium hydride from hydrogen and metallic iridium at a pressure of 55 gigapascals (GPa), corresponding to approximately 550,000 times the Earth's atmospheric pressure.
The new material can store up to three times more hydrogen than most other metal hydrides, and its synthesis may contribute to the development of high-capacity hydrogen fuel cells in cars and other applications.
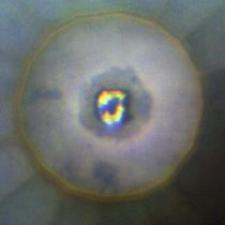 Formation of iridium trihydride inside a diamond anvil cell at a pressure of 100 GPa (gigapascals). The dark area at the center is iridium trihydride, the yellow areas are hydrogen. Credit: Thomas Scheler/University of Edinburgh
Formation of iridium trihydride inside a diamond anvil cell at a pressure of 100 GPa (gigapascals). The dark area at the center is iridium trihydride, the yellow areas are hydrogen. Credit: Thomas Scheler/University of Edinburgh
The researchers from Edinburgh University (UK), Oviedo University (Spain) and DESY also showed that iridium hydride has an unexpected structure that does not occur in other known hydrides. Since a material's structure determines its mechanical and electronic properties, the new structure could potentially lead to the discovery of unprecedented properties. The study was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Chemical compounds of metals and hydrogen, called metal hydrides, are promising candidates for industrial hydrogen storage. Once hydrogen is released from the hydride, it can be further used to produce electricity in an environmentally friendly manner such as in fuel-cell-driven vehicles. "In a broader sense, our research aims at a deeper understanding of how metal hydrides form and how the hydrogen can subsequently be extracted again," explains Thomas Scheler, the study's first author and former PhD student of Eugene Gregoryanz's group at Edinburgh University.
Another important application is the potential of metal hydrides to act as superconductors, i.e. materials that conduct electric currents without electrical resistance below a critical temperature. Such behavior has been observed or predicted for the hydrides of the noble metals palladium and platinum, for instance, and may also occur in the hydrides of other chemically related noble metals such as iridium. However, iridium hydride had never been observed prior to this study, and the researchers consequently set out to synthesize it for the first time.
At PETRA III's experimental station P02 for extreme conditions research, the scientists placed a piece of iridium inside a pressure cell, known as diamond anvil cell, which they subsequently loaded with hydrogen. The research team then compressed the sample using pressures as high as 125 GPa. Simultaneously, PETRA III's intense and bundled X-rays traversed the sample and revealed its structural changes with varying pressure.
"At 55 GPa, we observed new X-ray signals, which do not stem from metallic iridium and which became stronger and stronger with increasing pressure," explains Gregoryanz. The researchers concluded that iridium hydride had indeed formed as a new material phase.
However, the signals of the hydride were obscured by signals from residual iridium still present in the sample. "We therefore employed laser heating of the sample, which helped with the synthesis of iridium hydride," says DESY researcher Zuzana Konôpková. In the laser-heated sample, the hydride formed much faster without leaving residual iridium behind.
"Laser heating was only one of several experimental conditions that were crucial for the success of our experiments," adds Scheler. "The availability of fast detectors and high X-ray energies at P02 as well as PETRA III's extremely focused X-ray beam contributed as well."
When analyzing their data, the researchers noticed that the newly formed iridium hydride phase had an unusual structure. Normally, the formation of metal hydrides involves the widening of a metal's inner structure with hydrogen occupying the intermediate space between metal atoms. In these hydrides, hydrogen is not bound to the metal and typical hydrogen-to-metal ratios are close to 1.
In contrast, hydrogen becomes part of the crystal lattice in iridium hydride and forms a structure not observed in any other hydride. "Our X-ray data suggest that the iridium atoms occupy the corner positions of a cube while hydrogen is located at the center of the faces in the simple cubic lattice," says Scheler. As a result, each iridium atom is surrounded by three hydrogen atoms, resulting in an iridium trihydride phase that can store up to three times more hydrogen than most other metal hydrides.
However, the identification of iridium trihydride from the X-ray data alone remains indirect because it can only be inferred from hydrogen-induced movements of the iridium atoms. "Hydrogen itself, which is the lightest of all elements, is almost invisible to X-rays and we cannot determine its positions directly," explains Konôpková. Therefore, the researchers performed additional theoretical calculations, which supported the presence of a simple cubic lattice, albeit distorted, in iridium hydride.
The present study could potentially impact future developments of hydrogen-storage and hydrogen-fuel-cell technologies. Although iridium is too rare and too expensive for routine industrial applications, the synthesis of a novel iridium hydride material with a new structure and high hydrogen content may aid the search for other high-capacity metal hydrides. Moreover, future research has yet to uncover iridium hydride's mechanical and electronic properties. "Our experiments revealed the material's structure," Gregoryanz says. "This information can now be used for theoretical predictions of its properties, including superconductivity."
Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY is the leading German accelerator centre and one of the leading in the world. DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and receives its funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (90 percent) and the German federal states of Hamburg and Brandenburg (10 percent). At its locations in Hamburg andZeuthen near Berlin, DESY develops, builds and operates large particle accelerators, and uses them to investigate the structure of matter. DESY's combination of photon science and particle physics is unique in Europe.