Mar 24 2014
KIT researchers have developed microstructured lightweight construction materials of highest stability. Although their density is below that of water, their stability relative to their weight exceeds that of massive materials, such as high-performance steel or aluminum. The lightweight construction materials are inspired by the framework structure of bones and the shell structure of the bees' honeycombs. The results are now presented in the journal PNAS, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1315147111.
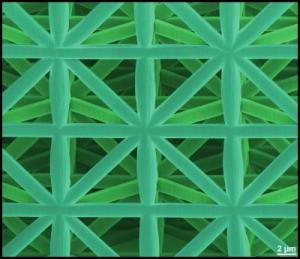 The framework construction made of a ceramic-polymer composite is highly stable, although the individual elements have a thickness of a few hundred nanometers only. Credit: Picture: J. Bauer/KIT
The framework construction made of a ceramic-polymer composite is highly stable, although the individual elements have a thickness of a few hundred nanometers only. Credit: Picture: J. Bauer/KIT
"The novel lightweight construction materials resemble the framework structure of a half-timbered house with horizontal, vertical, and diagonal struts," says Jens Bauer, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). "Our beams, however, are only 10 µm in size." In total, the lightweight construction elements are about 50 µm long, wide, and high.
"Nature also uses open-pore, non-massive structures for carrying loads," Oliver Kraft, KIT, explains. Examples are wood and bones. At the same density, however, the novel material produced in the laboratory can carry a much higher load. A very high stability was reached by a shell structure similar to the structure of honeycombs. It failed at a pressure of 28 kg/mm2 only and had a density of 810 kg/m3. This exceeds the stability / density ratio of bones, massive steel, or aluminum. The shell structure produced resembles a honeycomb with slightly curved walls to prevent buckling.
To produce the lightweight construction materials, 3D laser lithography was applied. Laser beams harden the desired microstructure in a photoresist. Then, this structure is coated with a ceramic material by gas deposition. The structures produced were subjected to compression via a die to test their stability.
Microstructured materials are often used for insulation or as shock absorbers. Open-pore materials may be applied as filters in chemical industry.