Aug 29 2015
A group at NIMS MANA has developed tissue adhesive porous films that promote angiogenesis without using growth factors. This new technology may contribute to medical cost reduction while maintaining the quality of medical treatment. This study was published in the online version of the academic journal Biomaterials on June 9, 2015.
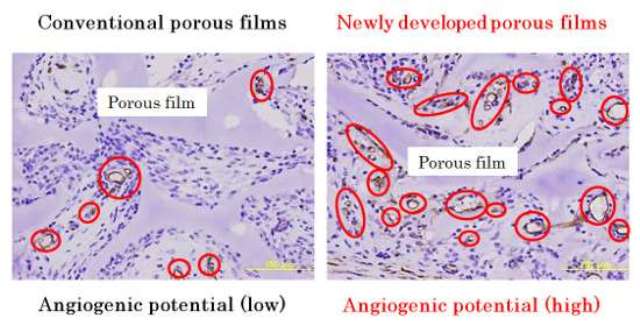 Rat tissues 7 days after subcutaneous implantation of porous films. Red circles indicate newly formed blood vessels. There were few newly formed blood vessels in the tissue treated with conventional porous films (left). In contrast, there were many blood vessels formed in the tissue treated with the newly developed porous films (right).
Rat tissues 7 days after subcutaneous implantation of porous films. Red circles indicate newly formed blood vessels. There were few newly formed blood vessels in the tissue treated with conventional porous films (left). In contrast, there were many blood vessels formed in the tissue treated with the newly developed porous films (right).
A research group led by Tetsushi Taguchi, a MANA Scientist at the Biomaterials Unit, International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (MANA), NIMS, has developed tissue adhesive porous films that promote angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) without using growth factors. This new technology may contribute to medical cost reduction while maintaining the quality of medical treatment without using growth factors that are expensive and prone to deactivation.
To promote angiogenesis in body parts where blood flow is poor due to diabetes, research has been conducted to develop materials that absorb growth factors and gradually release them. Studies also have been carried out to combine stem cells that produce growth factors and materials. Growth factors are able to effectively promote angiogenesis when released slowly from a material. However, they are expensive and have issues such as being prone to deterioration in terms of their cell proliferation effect. In addition, nearly no study has been conducted on tissue adhesive technology necessary to steadily fix a material containing growth factors on affected tissues.
In consideration of these issues, the research group developed porous films using pig-skin-derived gelatin chemically modified with hexanoyl group that is believed to provide superb tissue adhesiveness and excellent bonding to growth factors. With greatly increased porosity, the newly developed porous films demonstrated about five times greater angiogenic capability compared to conventional porous films. Furthermore, the new films exhibited about three times greater tissue adhesiveness than conventional ones.
The newly developed porous films do not require an addition of costly growth factors, and they are capable of adsorbing vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) that occur naturally in the body and taking them into the film materials. Then, the research group found that an enzyme produced in the body breaks down the porous films, which in turn slowly release VEGFs, thereby promoting angiogenesis. These results indicate that the application of porous films stimulates angiogenesis through improving the body's self-healing capacity.
This porous material alone is capable of boosting the formation of a blood vessel network without relying on growth factors that are expensive and prone to deactivation. Accordingly, expectations are high for the application of this technology, for example, to target legs of diabetes patients with poor blood flow and to effectively regenerate blood vessels. This technology also may contribute to cost reduction in certain medical treatments. Based on these positive results, the research group intends to engage in collaborative studies with medical and industrial sectors, and aims to expand its activities in the field of regenerative medicine and developing medical devices.
Explore further: Team designs a bandage that spurs, guides blood vessel growth
More information: "Enhanced angiogenesis of growth factor-free porous biodegradable adhesive made with hexanoyl group-modified gelatin." Biomaterials. 2015 Sep;63:14-23. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.003