The latest development, including essential oils for coating food products and their effects on shelf-life, has been reviewed by researchers in Applied Food Research.

Study: A comprehensive Review on the application of Essential Oils as Bioactive Compounds in Nano-emulsion based Edible Coatings of Fruits and Vegetables. Image Credit: Goncharov_Artem/Shutterstock.com
The demand for fresh fruit has risen immensely worldwide, with consumers wanting to gain the necessary supplements from these natural sources. However, the shelf-life of naturally grown fruit and vegetables is short, reducing their availability within supermarkets.
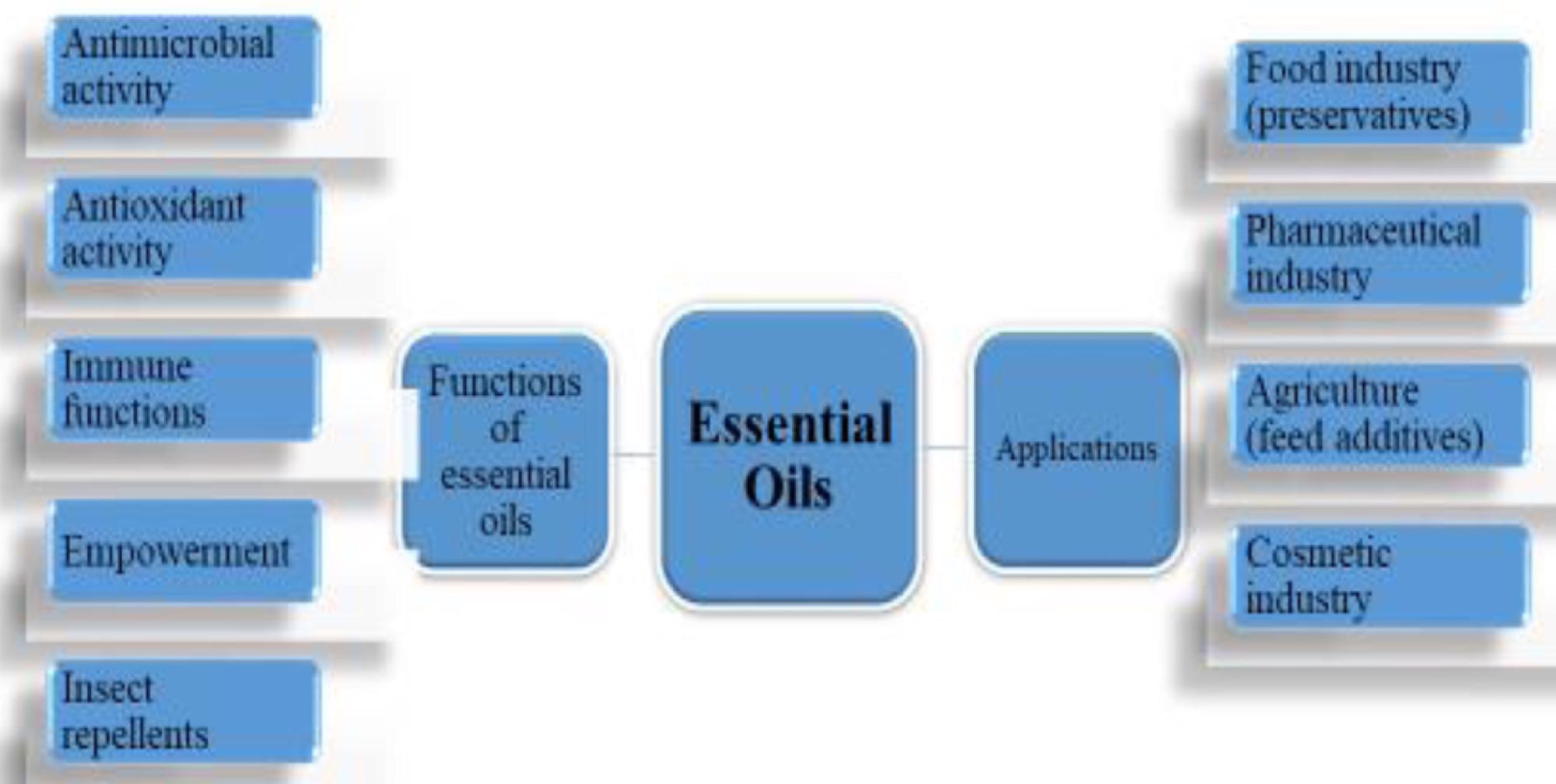 Various industrial applications of essential oils. © Pandey, V., Islam, R., Shams, R. and Dar, A., (2022)
Various industrial applications of essential oils. © Pandey, V., Islam, R., Shams, R. and Dar, A., (2022)
Interestingly, the use of edible coatings could potentially innovate this field. This technique could increase shelf-life and provide minimally processed fruits and vegetables a safe atmosphere free from microbial contamination. Additionally, this could also maintain the quality of these products through the regulation of moisture and gas transfer, including carbon dioxide and oxygen.
The use of edible film or coatings, either being covered by a thin sheet or being prepared within a liquid solution, can provide significant benefits to food products and their viability.
Benefits of Edible Film / Coating
Approaches to increasing the viability of fruits and vegetables can assist in preventing moisture, oxygen and constituent loss, and conserving the quality of food products closest to their original state.
These benefits analyzed by researchers have increased the attraction of future packaging, moving from synthetic materials to edible coatings; this would enable the control and reduction of deterioration while increasing quality maintenance, preservation and shelf-life. It would also be environmentally friendly and have a low cost.
These benefits would help aid the consumer demand for fruits and vegetables worldwide, as well as address the ongoing issue of food waste.
Plant Extract and Essential Oils within Edible Film
Essential oils have been utilized as food additives due to their antimicrobial effects and have been granted as being Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
With benefits such as being an antimicrobial, antioxidant and having bioactive compounds, they have garnered attention for use as a food preservative; however, with each essential oil and plant extract differing in biological activities and physiochemical properties and even aromas, being selective in which to use for certain food products is critical to ensure compatibility.
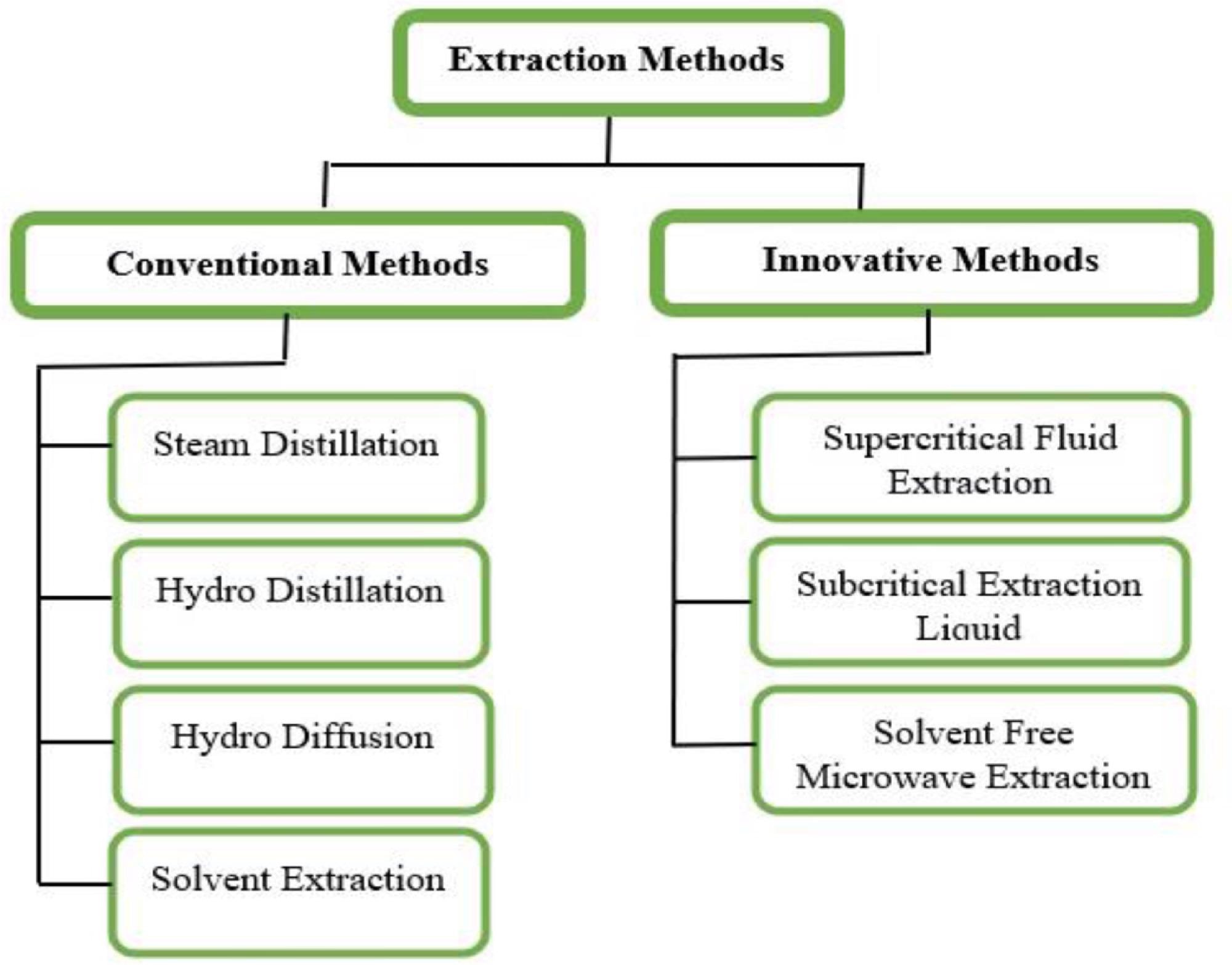
Different extraction methods of essential oil. © Pandey, V., Islam, R., Shams, R. and Dar, A., (2022)
An example of this can be seen with cinnamon essential oils being utilized within cosmetics and food as an antimicrobial plant extract additive. When it is incorporated within cyclodextrin nanosponges, it can be utilized as an antimicrobial food packaging product. Garlic essential oils have also been utilized within food packaging for their antimicrobial properties.
The innovative approach to incorporating essential oils within edible coatings can be a method to prevent the growth of mold and yeast. This technique would optimize and effectively increase the shelf-life of food products.
However, to further this research on food product preservation, nano-emulsions can also be used to create advanced edible coatings for longer-lasting fruit and vegetables.
Nano-emulsions
Nano-emulsions, which are oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsions can be a step towards improving the physiochemical properties of edible coatings for further quality control of food products.
These advanced coatings have been researched and found to improve the quality and sensory characteristics of fruit such as using a nano-emulsion within a pectin-based edible coating on freshly cut orange slices.
This next-generation of edible coatings may revolutionize the food industry to increase the viability of fruit and vegetables; this technique allows for these emulsions to fuse with the components easily.
Nano-emulsions, which are between 10 and 100nm, cover food-grade ingredients and are optically clear, differing them from traditional emulsions which are opaque, larger and less stable, causing them to break down over time.
Nano-emulsions are also more chemically reactive and have emulsifiers, maintaining their stability, with proteins, phospholipids, polysaccharides, surfactants that reduce interfacial tension.
Additionally, their increased surface area enhances their functionality and the functional qualities of their encapsulated product, resulting in the increase of quality within fresh food items. The nano droplet size of nanoemulsions also affects their ability to promote antibacterial essential oil characteristics and increase the absorption of hydrophobic compounds.
Future Outlook for Advanced Edible Coatings
These advanced coatings can be applied to various food products such as postharvest fruit, including mangos and strawberries, due to their ability to improve the dispersion of active chemicals.
Previous researchers have found nano-emulsions derived from chitosan, a useful nano-material, or nutmeg seed oil, can be used as an edible coating for strawberries specifically. This would increase the storage of this fruit for up to 5 days due to retaining its quality and decreasing microbial development.
Incorporating essential oils within nano-emulsions would also increase its functionality as an edible coating, due to its environmentally friendly characteristics and active components. This combination would aim to improve the antioxidant and antibacterial characteristics of edible coatings and reduce any effects of bacterial growth from Salmonella to E.coli.
Advanced edible coatings would revolutionize future storage of fresh food products, allowing them to be available to consumers for a longer period of time, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microbes. This kind of advanced packaging is cost-effective and would be a welcomed alternative for synthetic plastic packaging used in the food packaging industry, the highest contributor to plastic pollution.
Continue reading: Applying Nanoemulsions to the Food Sector.
Reference
Pandey, V., Islam, R., Shams, R. and Dar, A., (2022) A comprehensive Review on the application of Essential Oils as Bioactive Compounds in Nano-emulsion based Edible Coatings of Fruits and Vegetables. Applied Food Research, p.100042. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afres.2022.100042
Further Reading
Dhall, R., (2013) Advances in Edible Coatings for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 53(5), pp.435-450. Available at: https://doi.org/10.101610.1080/10408398.2010.541568
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.