The use of nanotechnology in Melatonin-based therapeutic agents to treat multiple disorders has been reviewed in a study published in Cancer Cell International.

Study: Nanotechnology-based advances in the efficient delivery of melatonin. Image Credit: Vikks/Shutterstock.com
Melatonin
Melatonin, or N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl], is a biogenic amine that is generated mainly by the pineal gland. Its broad range of biological functions, from insomnia to cancer and degenerative disorders, has illustrated its potential as a highly effective therapeutic agent.
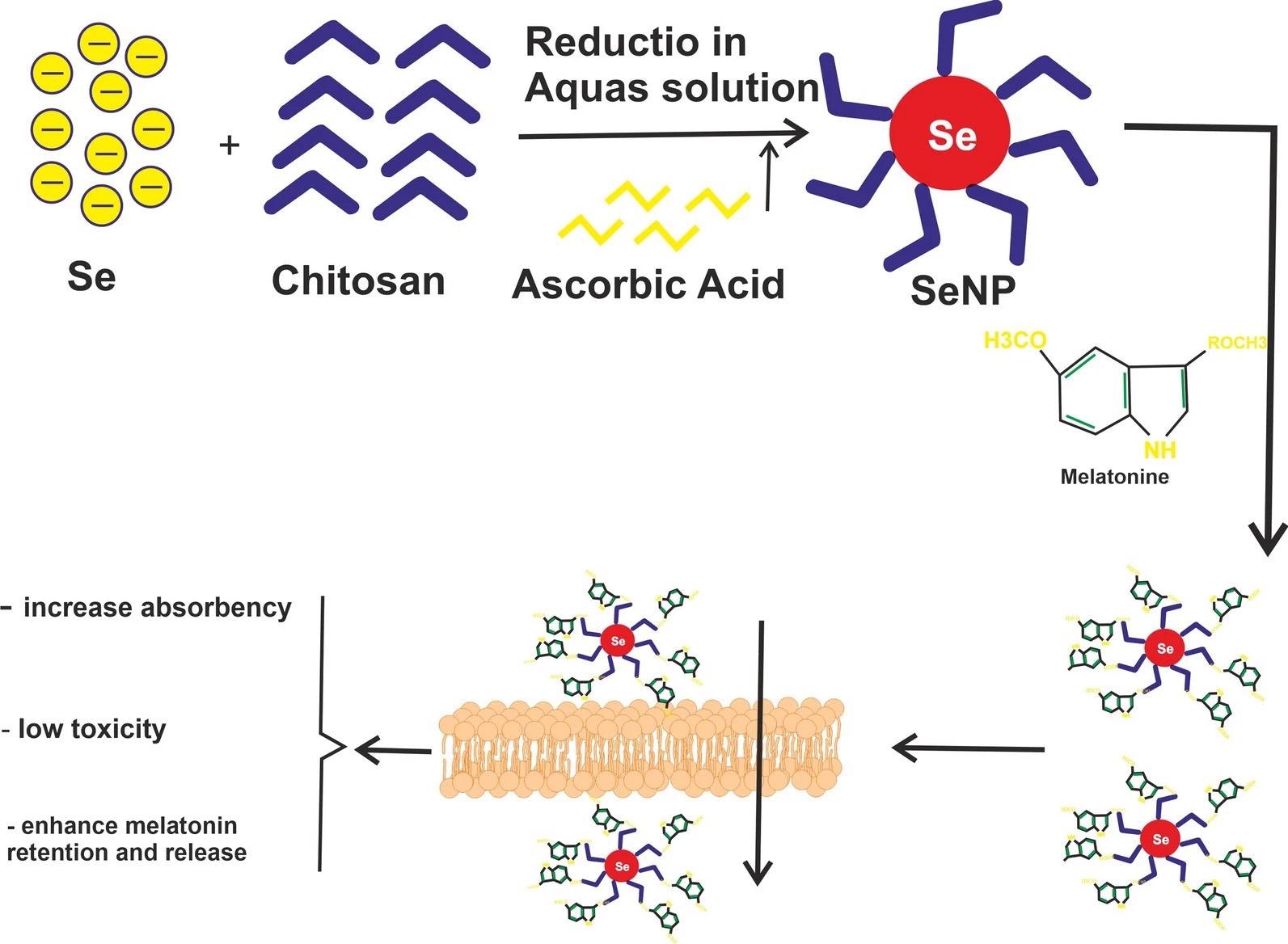
Figure 1. The schematic illustrates provided show melatonin selenium-based nanoparticle and its effects. © Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., Mihanfar, A., Yousefi, B. and Majidinia, M., (2022).
However, due to melatonin affecting receptors on the cellular membrane within the nucleus, it can act as an anti-oxidant molecule with unwanted effects being observed after administration.
Interestingly, the advancement of drug delivery through the use of nanotechnology would enable melatonin to be administered in a safer and more effective fashion.
The use of nano-delivery systems that carry melatonin ensures an increase in half-life as well as decreased toxicity. Additionally, the use of nanocarriers provides a biodegradable and efficient manner of delivery that can enhance the pharmacokinetic interactions of melatonin as a therapeutic agent, with enhanced patient compliance due to its high efficacy.
The use of melatonin as a therapeutic agent in this manner allows enhanced targeting of cellular pathways due to being delivered to specific areas, increasing the effectiveness of this hormone within the target organ, and reducing systemic side effects to peripheral tissue.
Nanotechnology-based Drug Delivery Systems
Research into novel drug delivery systems has included the use of nanotechnology and biomaterials and has increased the efficacy of drugs, advancing the use for delivering melatonin in a more efficient approach.
Nanoparticles that are within the nanoscale of 1 and 100 nm in size can consist of a range of biodegradable components that include, polymers, lipids, metals and more.
The use of these nanocarriers can prove to be useful due to the natural interaction with biological systems, enabling efficient selectivity and delivery and ultimately increasing therapeutic outcomes.
Selenium
Selenium, an essential trace element, used to build selenoproteins which have high enzymatic activity, has been used to create nanoparticles (SeNPs).
These particles have resulted in significant anti-cancer effects, with research into use as a monotherapy as well as a combined therapy for use as a drug delivery nanosystem for cancer therapeutics.
Interestingly, the incorporation of melatonin and SeNPs has illustrated beneficial synergy, with a combination of the two agents resulting in a significant reduction of damage that was caused by immunological response followed by a BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) administration to liver cells within mice.
This combined treatment that utilized melatonin was also found to reduce the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) after BCG exposure within a separate study.
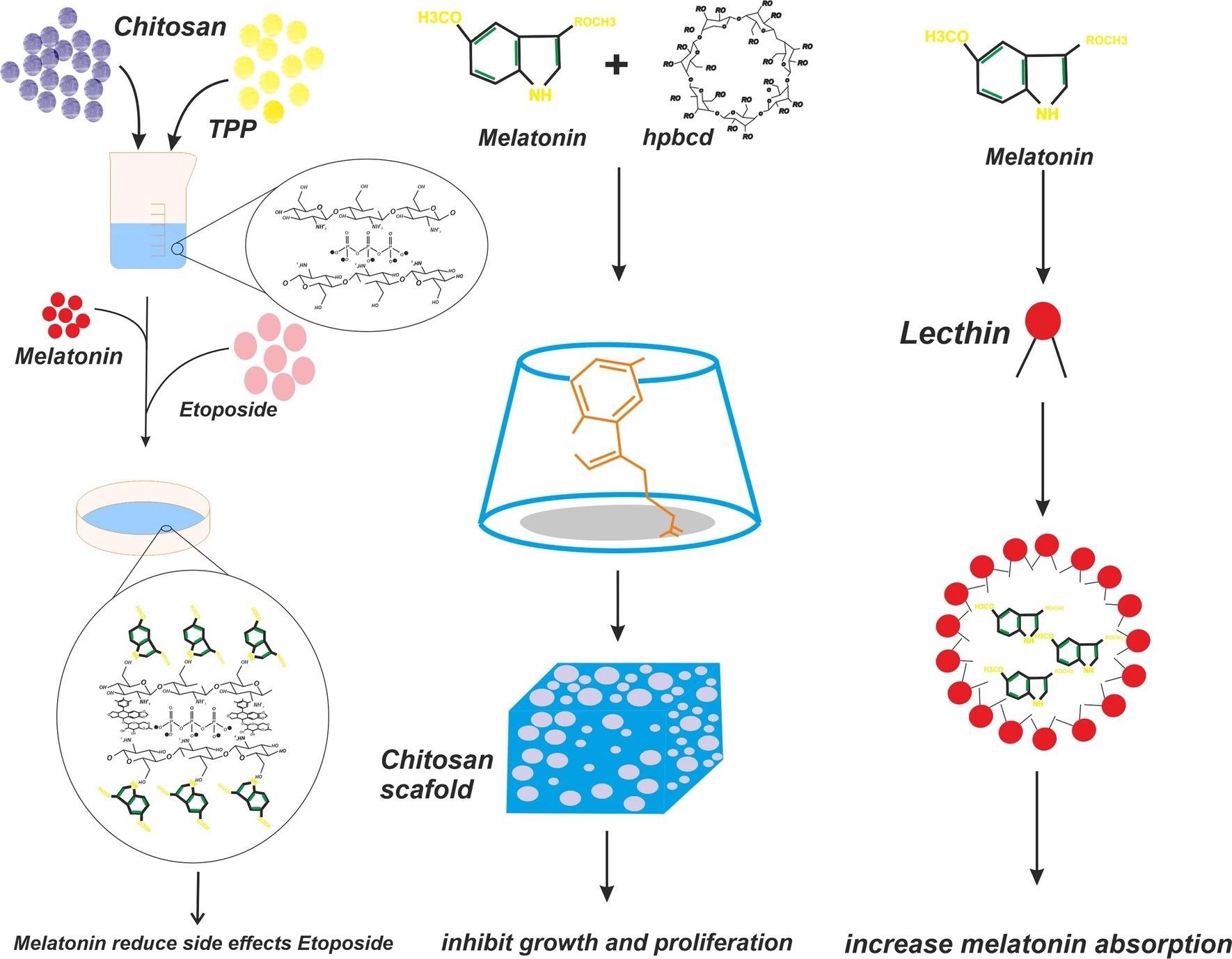
Figure 2. The schematic diagram provided reveals melatonin chitosan nanostructures and its functions. © Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., Mihanfar, A., Yousefi, B. and Majidinia, M., (2022).
Chitosan
The significant reduction of DNA damage and ROS formation can also be seen with previous research that utilizes chitosan nanoparticles as a nano-drug-delivery system that delivered melatonin to HepG2 cancer cells.
These cancer cells were undergoing treatment with etoposide, a topoisomerase II inhibitor that is genotoxic in nature and the aim of including melatonin was to evaluate its beneficial effect in reducing damage from the cancer treatment.
The most significant findings from this research consisted of a group of cells undergoing melatonin treatment 24 hours prior to receiving etoposide treatment.
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
Additionally, research into the pharmacokinetics of administered melatonin through the use of solid lipid nanoparticles (SNLs), which have exceptional penetration abilities, including hydrophobic barriers and the central nervous system, have also found increased serum levels through this nanotechnology approach.
This technique utilized oral and transdermal administration of this SNL-melatonin complex and resulted in melatonin levels within plasma being elevated over 50 pg/ml for approximately 24 hours after only administering 3 mg of melatonin in this nanocarrier form.
Translational Significance
With melatonin having a short half-life and being quickly eliminated from the body’s circulatory system, the time it requires to take effect for the treatment of disorders can be inefficient.
Additionally, its limited absorption from mucosal and dermal surfaces is also another challenge for convention drug delivery systems involving the administration of melatonin.
The research carried out on delivering melatonin through this nanotechnology format has illustrated the potential of increasing its presence within the circulatory system as well as its impact on improving anti-cancer treatments.
Additionally, its use within conventional applications such as insomnia, jetlag and sleep disorders may be improved with sustained delivery through this novel nanotechnology delivery system.
With clinical trials for this hormone for multiple disorders from neoplastic conditions to degeneration, the potential for melatonin within healthcare and medicine can be significant.
However, research on nanoparticle delivery of melatonin is still within its early stage with limited in vitro delivery and models of human conditions; the significant translation of this research would require further studies that evaluate safety as well as cost efficiency for human administration.
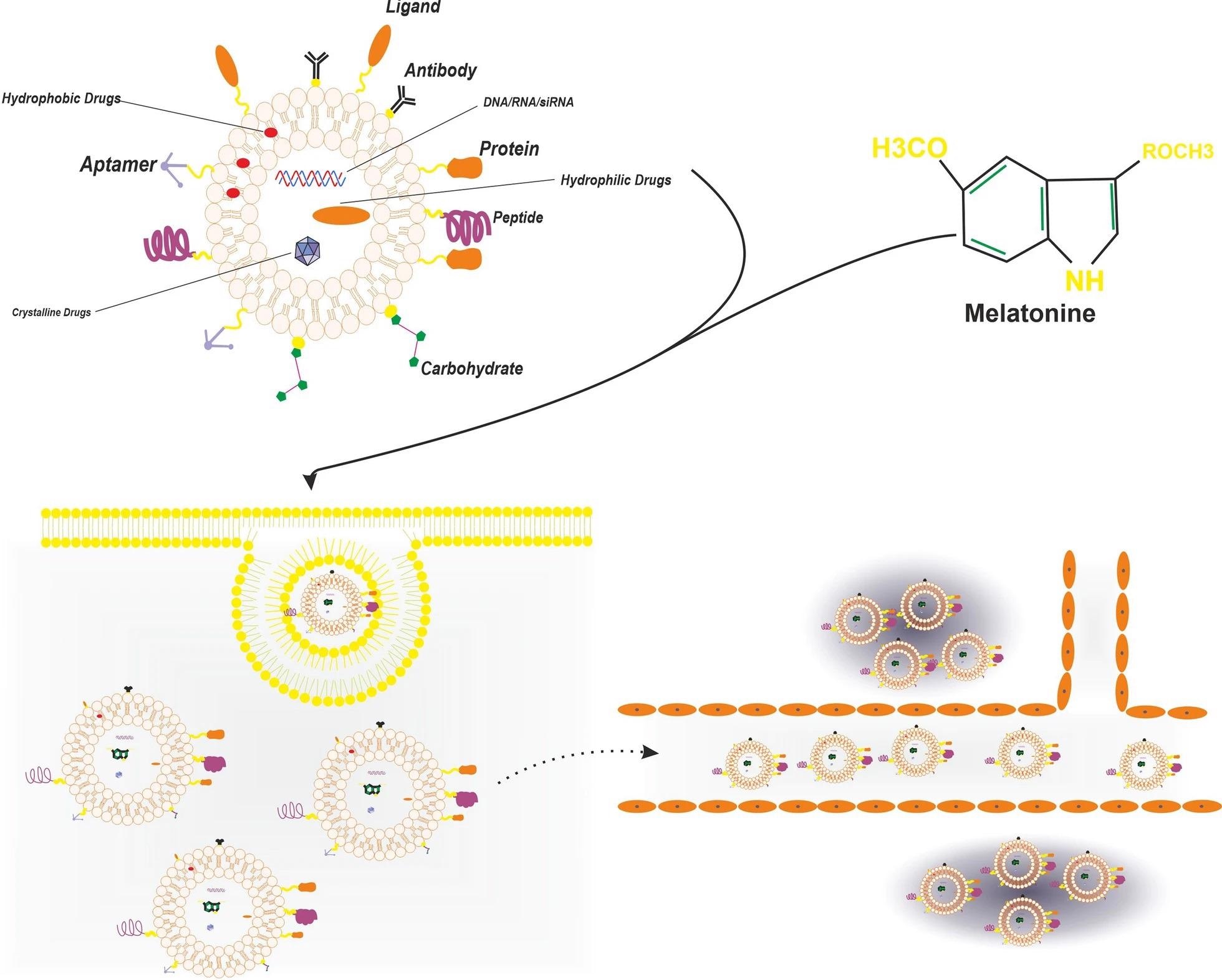
Figure 3. The figure shows the liposome as delivery vehicle for melatonin, liposome increase the transdermal delivery of melatonin and also increase distribution of melatonin in multiple part of body like cornea as fragile site. © Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., Mihanfar, A., Yousefi, B. and Majidinia, M., (2022).
Reference
Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., Mihanfar, A., Yousefi, B. and Majidinia, M., (2022). Nanotechnology-based advances in the efficient delivery of melatonin. Cancer Cell International, 22(1). Available at: https://cancerci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12935-022-02472-7
Further Reading
Talib, W., Alsayed, A., Abuawad, A., Daoud, S. and Mahmod, A., (2021). Melatonin in Cancer Treatment: Current Knowledge and Future Opportunities. Molecules, 26(9), p.2506. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092506
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.