Due to its vast range of applications in brackish water and seawater desalination, reverse osmosis (RO) has received a lot of attention. The primary products in this industry are thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide (PA) RO membranes, which have a dense separation layer and a porous support layer.
Image Credit: Vink Fan/Shutterstock.com
The widespread use of TFC PA RO membranes is, however, constrained by the comparatively poor permeability-selectivity of PA RO membrane and membrane fouling of TFC RO membrane.
It has been shown that the creation of nanocomposite membranes is a great way to combine the benefits of polymers and inorganic nanoparticles. By fine-tuning the composition and structure, RO membrane’s natural performance might be increased.
For instance, to create water transport channels, hydrotalcite (HT) was mixed with an aqueous solution and added to the PA matrix during the interfacial polymerization stage. High perm-selectivity was demonstrated by the developed membrane with improved water flux without sacrificing salt rejection.
Additionally, it has been demonstrated that membrane modification, such as the insertion of nanoparticles, surface coating, and grafting, is an effective method of preventing biofouling.
One such method to give RO membranes anti-biofouling capabilities without causing harm to the PA matrix is to graft anti-biofouling chemicals onto nanoparticles embedded in the PA matrix.
The abundance of hydroxyls in HT nanoparticles can react with siloxy or silane coupling agents to facilitate anti-biofouling grafting.
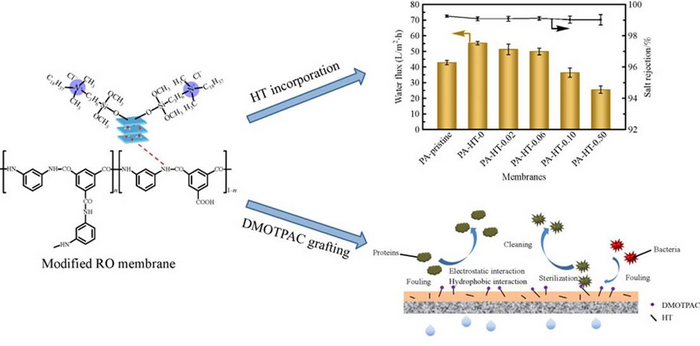
Image Credit: Xinxia Tian , Hui Yu , Jun Yang , Xiaotai Zhang, Man Zhao , Yang Yang , Wei Sun, Yangyang Wei , Yin Zhang, Jian Wang , Zhun Ma
Therefore, by using HT nanoparticles as dopants in the PA layers and grafting silane coupling agents with anti-biofouling functional groups on the membrane surface, novel TFC RO membranes with high perm-selectivity and anti-biofouling capability can be produced.
Prof. Jian Wang from the Institute of Seawater Desalination and Multipurpose Utilization, Prof. Zhun Ma from the Shangdong University of Science and Technology, Dr. Xinxia Tian from the Institute of Seawater Desalination and Multipurpose Utilization, and their team members collaborated to develop novel RO membranes with prolonged and stable high performance.
They were inspired by the properties of HT nanoparticles and silane coupling agents containing quaternary ammonium.
Their work significantly strengthens TFC PA RO membrane performance and offers helpful technical advice for desalination in the future. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering published this study’s findings in 2022,
By dispersing the Mg-Al-CO3 HT nanoparticles in organic solutions, they were added to the PA layers in this work during interfacial polymerization. Incorporating HT had two purposes: it improved water flux and served as grafting sites.
To make up for the loss brought on by the subsequent grafting process, the HT inclusion enhanced the water flux without reducing salt rejection.
Anti-biofouling agent dimethyloctadecyl [3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ammonium chloride (DMOT-PAC) was grafted onto the exposed surface of HT. High perm-selectivity and anti-biofouling capabilities were added to RO membranes using the combination of HT integration and DMOTPAC grafting.
In comparison to the pristine membrane, PA-HT-0.06 had a water flux of 49.8 L/m2•h, a 16.4% increase. The 99.1% salt rejection of PA-HT-0.06 was equivalent to the pristine membrane.
Regarding the fouling of negatively charged lysozyme, the modified membrane’s water flux recovery was higher than the pristine membrane’s (for example, 86.8% of PA-HT-0.06 compared to 78.2% of PA-pristine). PA-sterilizing HT-0.06’s efficiency for E. coli and B. subtilis were 97.3% and 98.7%.
The development of covalent bonds between DMOTPAC and HT nanoparticles implanted in PA matrix to produce RO membranes with strong perm-selectivity and anti-biofouling capabilities is the first to be reported in this study.
The development of RO membranes with strong perm-selectivity and anti-biofouling qualities is assured by the introduction of nanoparticles and functional group grafting.
Journal Reference
Tian, X., et al. (2022). Preparation of reverse osmosis membrane with high permselectivity and anti-biofouling properties for desalination. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering. doi:10.1007/s11783-021-1497-0.