Water insolubility is one of the major disadvantages of quantum dots that make them unsuitable for biological and medical applications.
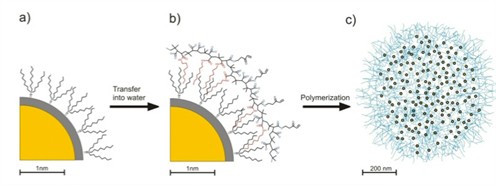 Quantum dots made water-soluble by a coating can, in turn, be combined with polymers and be coupled to other quantum dots
Quantum dots made water-soluble by a coating can, in turn, be combined with polymers and be coupled to other quantum dots
To overcome this drawback, scientists at the Singapore-based A*STAR agency and at the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology of the University of Twente have created a coating that makes the nano-scale light sources soluble in water.
Thus with the help of the coating, quantum dots can now be utilized within the human body, and even within living cells. In addition to enhancing solubility in water, the novel coating allows other molecules to bind on its surface, thus the coated quantum dots are now capable of binding with certain types of cells like tumour cells.
The scientists have reported about their coating material in the Nature Protocols journal. The research work is a joint study between the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering of the A*STAR agency and the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology of the University of Twente.
Quantum dots are a better choice compared to fluorescent tags that are being used for investigating biological processes. The semiconductor nanostructures release long-lasting bright lights with different colors that vary with the quantum dots’ size. Quantum dots were earlier not suitable for utilization in living organisms for several causes, including their toxicity.
The scientists have developed a polymer coating with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties called an amphiphilic coating. The hydrophobic end of the polymer material is bonded to the surface of the quantum dots, while its hydrophilic side enables the quantum dots to exhibit water solubility properties. The coating covers the quantum dot surface via a self-assembly process and has less impact on the light-emitting properties of the quantum dots.