May 27 2013
More effective detection and diagnosis of oral cancer could result from an advance in noninvasive imaging of epithelial tissue by a Texas A&M University researcher who says her research has the potential to change the way doctors initially look for precancerous and cancerous areas in a patient’s mouth.
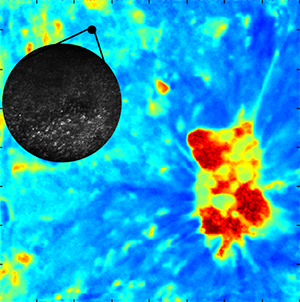 [Fluorescence lifetime imaging with a 16x16 mm2 field of view detects tissue biochemical changes on the macroscopic scale, and (inset) confocal microscopy with a 0.4 mm diameter field of view is used to characterize size, shape, and spacing of cell nuclei to detect oral precancer and cancer.]
[Fluorescence lifetime imaging with a 16x16 mm2 field of view detects tissue biochemical changes on the macroscopic scale, and (inset) confocal microscopy with a 0.4 mm diameter field of view is used to characterize size, shape, and spacing of cell nuclei to detect oral precancer and cancer.]
The imaging technique, which is detailed in the “Journal of Biomedical Optics,” is being developed by Kristen Maitland, assistant professor in the university’s Department of Biomedical Engineering. It combines two separate technologies -- confocal microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging –- to noninvasively evaluate both the structural changes of tissue as well as molecular changes that take place on a cellular and tissue level. These morphological and biochemical changes are key factors in determining if tissue is precancerous or cancerous, Maitland says.
Typically, such evaluations are made from lab analysis of biopsies, small amounts of surgically removed tissue. The challenge for doctors, Maitland says, is determining from what areas to take a biopsy. These determinations, she says, are largely based on visual evidence. In other words, doctors rely on the naked eye to look for problematic areas that warrant a biopsy. For doctors and patients both, it’s a bit of an educated guessing game. A biopsy from one area could be negative for cancer, but the tissue around it could be cancerous and remain undiagnosed.
That’s even more of a concern when it comes to oral cancer examinations, Maitland says. Visually determining the areas that warrant a biopsy can be difficult, she explains, because a patient’s mouth can manifest large, heterogeneous lesions that may be both benign and precancerous, which are indistinguishable by eye. Her system is designed to more precisely guide doctors to the troubled areas of a patient’s mouth through the use of optical images.
Noninvasive Detection of Oral Cancer Using Optical Imaging Techniques
“We want to enhance a doctor’s ability to detect the worst state of disease in the mouth,” Maitland says. “This is about increasing the diagnostic yield. For example, rather than taking a few biopsies from random sites to represent a large heterogeneous lesion, our system can guide the clinician to biopsy the tissue with the worst state of disease to provide a more accurate diagnosis, as opposed to possibly missing the cancer or precancer.”
Working with Associate Professor Javier Jo, Maitland has paired two different types of imaging technologies into a single imaging system that makes use of macroscopic and microscopic approaches to produce a detailed analysis of tissue.
One technology, known as fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM), enables Maitland and Jo to image large areas of oral tissue with ultraviolet light in a manner that shows signs of the molecular changes associated with precancer and cancer, revealing potential trouble areas. It’s overall effectiveness, however, is limited because FLIM can be “fooled” by inflamed tissue, which has a similar fluorescent signature to precancer, Maitland notes. To overcome this limitation, Maitland paired the technology with another technology known as confocal microscopy.
In contrast to FLIM, which focuses on greater areas of tissue, confocal microscopy is a single-point measurement (about 0.5 mm in this case) with a high sensitivity, Maitland says. It provides information about the morphological features of tissue – the same types of features a pathologist would examine in a histology section, such as the nuclear size of the cells and how densely packed the cells appear – important indicators of precancer, she notes. But just like FLIM, confocal microscopy has its own limitations, namely an incredibly small field of view (it’s not much bigger than the tip of a pencil). This limited field of view makes it difficult, if not impossible, to image an entire oral cavity with this technology – that’s where FLIM technology comes in, acting as a guide for the confocal microscopy utilized in this approach, Maitland explains.
“We think the combination of these two systems will address the limitations of other optical systems, she says. “Think of the fluorescence imaging as being used for screening and the confocal microscopy being used for diagnosis. A doctor or dentist would first find the abnormal area with the fluorescence and then go in with the confocal to make the diagnosis because it’s a more specific technique.”
So far, the results have been promising. Maitland has been able to combine the two systems so that the macroscopic and microscopic images produced from each technology can be co-registered, meaning she can correlate those images to the same point on the tissue. Equally as important, each imaging technique is contributing valuable information, she notes.
“We’ve been able to get macroscopic images with the FLIM that show clear differences in signal and spatial features due to biochemical changes in the tissue that correlate with precancer, or the development of cancer,” Maitland says. “With the confocal microscope, we’re able to see changes in the nuclear size, and we have the necessary resolution and the depth of imaging that is required to characterize epithelial changes.”
Maitland cautions that there is still work to be done before this system proceeds to large-scale clinical trials. Her team is working to obtain more data points before claiming the sensitivity and specificity required from a system such as this. She’s in the process of analyzing additional data from a hamster model of oral cancer and working with the Baylor College of Dentistry to evaluate her imaging system on samples of human oral biopsy tissue.
“The hope is we develop a system that is in real time, so it provides accurate diagnostic feedback almost instantaneously, whereas the processing needed for traditional histopathology can commonly take up to a week or two,” Maitland says. “A system like ours could empower doctors with the ability to determine treatment right away rather than having a patient come back weeks later to be treated. It also would enable doctors to noninvasively monitor treatment in order to determine its effectiveness on the diseased tissue.”