Apr 18 2016
In this study, Dr. Diana and her team of researchers present an inexpensive method suitable to develop microfluidic devices used in the biomedical field. Even though soft-lithography is the commonly used method to fabricate biomedical microdevices, it is still a time-consuming and expensive method. The growth in developing milling tools that are smaller than 100 µm, has resulted in the use of micromilling machines to produce microfluidic devices that have the ability to execute the cell separation process.
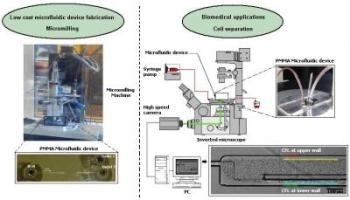 Recently, researchers were able to produce milling tools smaller than 100 m and consequently have promoted the ability of the micromilling machines to fabricate microfluidic devices capable of performing cell separation. (Dr. Diana Pinho, Bentham Science Publishers)
Recently, researchers were able to produce milling tools smaller than 100 m and consequently have promoted the ability of the micromilling machines to fabricate microfluidic devices capable of performing cell separation. (Dr. Diana Pinho, Bentham Science Publishers)
The researchers highlight a micromilling machine’s ability to fabricate microchannels down to 30 µm, and also the ability of the manufactured microfluidic device to partially separate the red blood cells from plasma. The team used a high-speed video microscopy system to carry out blood flow visualization and measurements of the free layer thickness of the cell. The researchers also demonstrated the limitations and advantages of the described micromilling fabrication technique to develop microfluidic devices, which can be used in cellular-scale flow studies.