Mar 20 2019
Researchers used nanoparticles comprising Fe and Ni as catalysts in the generation of hydrogen fuel by water electrolysis and found them to be more productive and successful compared to other high-cost materials.
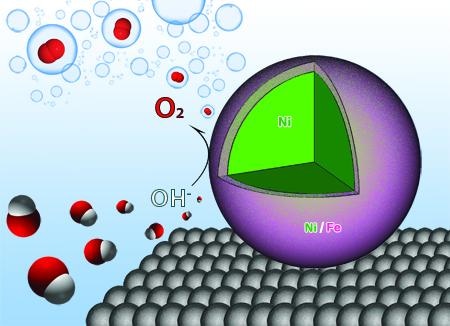 Researchers at the University of Arkansas have designed nanoparticles that act as catalysts, making the process of water electrolysis more efficient. (Image credit: Jingyi Chen, Lauren Greenlee, and Ryan Manso)
Researchers at the University of Arkansas have designed nanoparticles that act as catalysts, making the process of water electrolysis more efficient. (Image credit: Jingyi Chen, Lauren Greenlee, and Ryan Manso)
This invention was made by researchers from the University of Arkansas, namely, Jingyi Chen, associate professor of physical chemistry, and Lauren Greenlee, assistant professor of chemical engineering, and coworkers from Brookhaven National Lab and Argonne National Lab.
The research team showed that the use of nanocatalysts comprising Ni and Fe has increased the efficiency of water electrolysis, a process in which water atoms are split into hydrogen and oxygen and then form hydrogen gas on combining with electrons.
Chen and her team discovered that when nanoparticles composed of a Ni and Fe shell around a Ni core are used in the process, they react with the oxygen and hydrogen atoms and weaken the bonds, thus enhancing the efficiency of the reaction by enabling the production of oxygen more easily. Also, Fe and Ni cost less when compared to other catalysts, which are produced from rare materials.
This signifies a step toward rendering water electrolysis a more feasible and affordable technique for generating hydrogen fuel. Existing water electrolysis methods are more energy-intensive to be efficient.
Recently, Chen, Greenlee, and their coworkers published their findings in Nanoscale.
This research work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy.