A new approach for using the sol-gel process to change titania nanoparticles during their synthesis level to develop UV protection, antimicrobial, and super-hydrophobicity textile materials has been detailed in the journal Materials.

Study: Single Step Synthesis and Functionalization of Nano Titania for Development of Multifunctional Cotton Fabrics. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock.com
Textile's Surface Treatment to Have High Performance
Surface treatment of textiles via physical and chemical processes is critical in developing high-performance textile materials. The final features of the developed material determine the dynamic performance of textiles for a specific application.
Researchers have already been attempting to develop high-performance textile products using nanomaterials in recent years. As an outcome, new properties have indeed been imparted, enabling the development of textile materials.
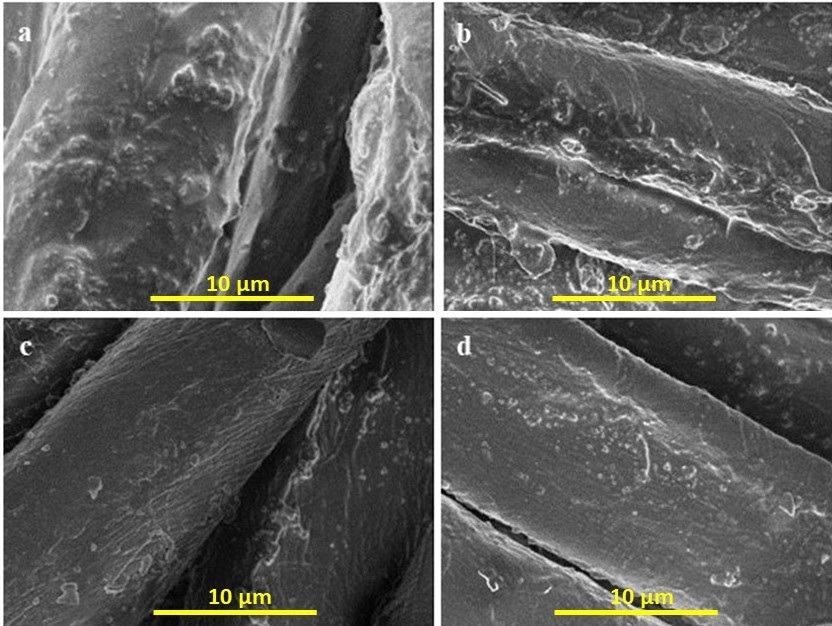
SEM images of coated cotton fabrics (a) unwashed sample (b) after 5 washing cycles. (c) after 10 washing cycles (d) after 20 washing cycles. © Safdar, F., et al. (2021).
As a result, nanomaterials are becoming increasingly important in the commercial development of multifunctional product lines.
Because of nanoparticles' large surface area and high surface energy, promising characteristics of nanostructured modified textiles such as UV protection, antimicrobial, and self-cleaning can be accomplished without considerably impairing breathability or hand feel.
Titanium as Various Application
Because of every day applications in various fields, polymeric cotton fabrics with self-cleaning, UV guarding, and antimicrobial activities have gained increased attention. The outer layer of cotton fabrics has also been modified with various nano-scale materials such as titania, silica, zinc oxide, and silver to achieve multifunctionality.
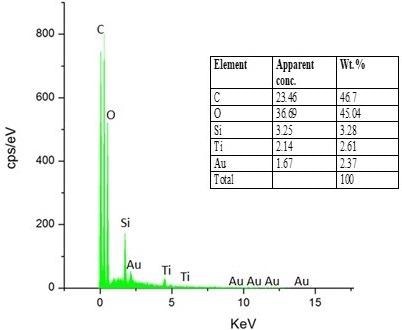
EDX spectra of cotton fabric treated with functionalized nano titania. © Safdar, F., et al. (2021).
Titania nanoparticles, for instance, have been extensively studied for their potential to instill UV protection, antimicrobial, and self-cleaning characteristics to fabrics. Titania-based nanoparticles are famous due to their remarkable catalytic properties under sunshine, as well as excellent properties such as hypoallergenic, cost-efficiency, and chemical resistance.
Rutile, anatase, and brookite are the three recognized crystalline phases of nano titania. The anatase phase has received the most attention due to its exceptional photocatalytic properties.
Titania Nanomaterials Creation Method
Titania nanomaterials can be created using a variety of techniques, including sol-gel, solvothermal, hydrothermal method, and emulsion precipitation. A few of these processes' limitations include high costs, longer reaction times, and complexity with many steps.
Concentration of the solution, pH, response time, and homogeneous distribution of the solution are all important factors that could affect the size of the particles, crystal structure, and morphological characteristics of as-synthesized nanoparticles.
Because of its simplicity, inexpensiveness, and high yield, the sol-gel method is the most commonly used method for preparing nano-titania.
In general, there are two types of sol-gel techniques: aqueous-based techniques and non-aqueous-based. Titania nanoparticles with varying morphologies can be created using a solvent with varying polarity, including a polar or non-polar solvent. The aqueous-based sol-gel model is the most commonly used method for producing titanium oxide nanomaterials.
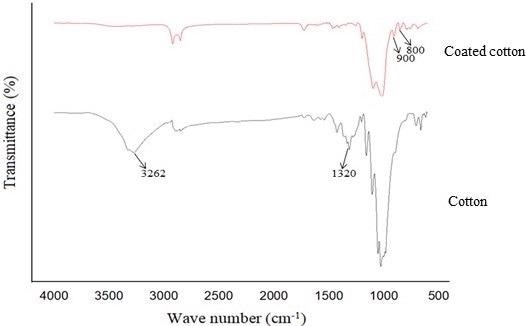
FTIR of treated cotton fabric with modified nano titania. © Safdar, F., et al. (2021).
The Advantage of Using Titania Nanoparticle
Titania nanomaterials prepared using the sol-gel method were used to impart different properties to the fabrics. Furthermore, such a process is straightforward to control, low cost and the particles produced are pure. Cotton fabrics' hydrophobic characteristics, among other characteristics, are quickly being one of the most important properties of fabrics.
Nano-roughness can be produced in two ways to alter surface characteristics: using nanoparticles and through various processing techniques such as the sol-gel method.
Limitations
The method for modifying cotton fabric, on the other hand, was complicated, time-consuming, and involved numerous steps. Furthermore, limitations include particle agglomeration, which hinders uniform dispersion and necessitates the use of specialized equipment.
Research Result Shows High UV Protection and Self Cleaning Textiles
The strong multifunctional fabric was created by synthesizing modified hydrophobic nano titania in a single bath. The presence of GPTMS on the exterior of nano titania has been responsible for the increased longevity of functional characteristics such as UV protection, antimicrobial activities, and physical self-cleaning, which mimicked the self-cleaning characteristics of the lotus leaf after application on cellulosic material.
Because of the existence of epoxy and siloxane groups, the coating can be implemented to substrates containing amide, amine, and hydroxyl groups under appropriate conditions. A maximum of 220 UPF values were achieved for UV protection, and excellent UV safeguards were maintained after multiple washing cycles. The coated substrate's average bacterial reduction was observed from 99% to 93%.
All of the findings point to the creation of a multifunctional cellulosic substrate with UV protection, antimicrobial properties, and superhydrophobicity, as well as improved durability. The new further research can be more straightforward, time-saving, and suitable for industrial manufacture.
Continue reading: Medical Applications of Corrosion Resistant Modified Titanium Implants.
Reference
Safdar, F., et al. (2021). Single Step Synthesis and Functionalization of Nano Titania for Development of Multifunctional Cotton Fabrics. Materials, 15(1), 38. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/1/38
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.