Apr 29 2019
New research demonstrates that it is possible to program nanostructures made of DNA molecules to operate as pH-responsive cargo carriers, opening the door toward functional drug-delivery vehicles.
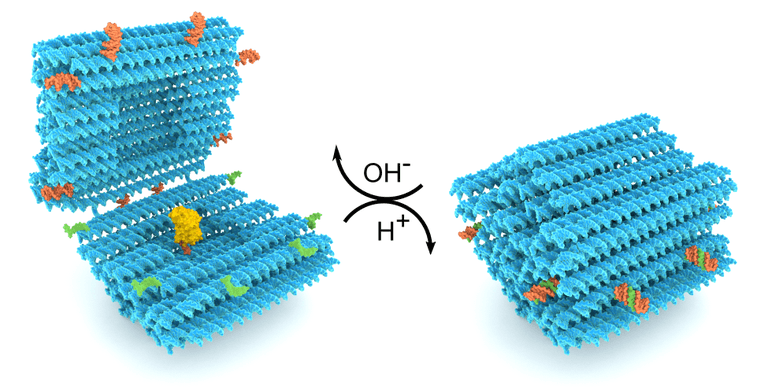 The pH-responsive DNA origami nanocapsule (blue) loaded with an enzyme (yellow color, high pH). (Image credit: Veikko Linko, Boxuan Shen, and Heini Ijäs/Aalto University)
The pH-responsive DNA origami nanocapsule (blue) loaded with an enzyme (yellow color, high pH). (Image credit: Veikko Linko, Boxuan Shen, and Heini Ijäs/Aalto University)
Scientists at the University of Jyväskylä and Aalto University in Finland have created a tailored DNA nanostructure that can carry out a predefined function in conditions similar to the human body. For this purpose, the group developed a capsule-like carrier that closes and opens based on the pH level of the nearby solution. The nanocapsule can be loaded or filled with a range of cargo, closed for delivery and opened again by a slight pH rise.
The role of the DNA nanocapsule is dependent on pH-responsive DNA residues.
In order to achieve this, the group developed a capsule-like DNA origami structure functionalized with pH-responsive DNA strands. Usually, such dynamic DNA nanodesigns are directed by the simple hydrogen-bonding of two complementary DNA sequences. In this case, one half of the capsule was attached with specific double-stranded DNA domains that could further create a DNA triple helix—in other words, a helical structure consisting of three, not just two, DNA molecules—by linking to an appropriate single-stranded DNA in the other half.
The triplex formation can happen only when the surrounding pH of the solution is right. We call these pH-responsive strands “pH latches” because when the strands interact, they function similarly to their macroscopic counterparts and lock the capsule in a closed state. We included multiple motifs into our capsule design to facilitate the capsule opening/closing based on the cooperative behavior of the latches. The opening of the capsule is actually very rapid and requires only a slight pH increase in the solution.
Heini Ijäs, Doctoral Student and Study First Author, Aalto University
Nanoparticles and Enzymes Could be Loaded and Encapsulated Within the Capsules
To make use of the nanocapsules for transporting molecular payloads or therapeutic substances, the group developed the capsule with a cavity that could accommodate various materials. They showed that both gold nanoparticles and enzymes could be loaded (high pH) and wrapped within the capsules (low pH) and represented (high pH) again. By tracking the enzyme activity, the scientists identified that the cargo remained completely operational across the course of the process.
The most intriguing thing about the DNA origami capsules is that the threshold pH at which the opening and closing take place is fully adjustable by selecting the base sequences of the pH latches. We designed the threshold pH to be 7.2-7.3, close to the blood pH. In the future, this type of drug carrier could be optimized to selectively open inside specific cancer cells, which can maintain a higher pH than normal healthy ones.
Veikko Linko, Adjunct Professor, Aalto University
In addition, the capsules remained operational at physiological magnesium and sodium concentrations, and in 10% blood plasma, and may remain operational even at higher plasma concentrations. On the whole, these findings help open the door for creating smart and fully programmable drug-delivery vehicles for nanomedicine.
The research was conducted in Professor Mauri Kostiainen’s laboratory and headed by Veikko Linko, both from Aalto University.