Aug 10 2009
If manmade devices could be combined with biological machines, laptops and other electronic devices could get a boost in operating efficiency. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have devised a versatile hybrid platform that uses lipid-coated nanowires to build prototype bionanoelectronic devices.
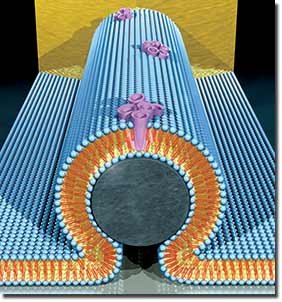 An artist's representation of a nanobioelectronic device incorporating alamethycin biological pore. In the core of the device is a silicon nanowire (grey), covered with a lipid bilayer (blue). The bilayer incorporates bundles of alamethicin molecules (purple) that form pore channels in the membrane. Transport of protons though these pore channels changes the current through the nanowire. Image by Scott Dougherty, LLNL
An artist's representation of a nanobioelectronic device incorporating alamethycin biological pore. In the core of the device is a silicon nanowire (grey), covered with a lipid bilayer (blue). The bilayer incorporates bundles of alamethicin molecules (purple) that form pore channels in the membrane. Transport of protons though these pore channels changes the current through the nanowire. Image by Scott Dougherty, LLNL
Mingling biological components in electronic circuits could enhance biosensing and diagnostic tools, advance neural prosthetics such as cochlear implants, and could even increase the efficiency of future computers.
While modern communication devices rely on electric fields and currents to carry the flow of information, biological systems are much more complex. They use an arsenal of membrane receptors, channels and pumps to control signal transduction that is unmatched by even the most powerful computers. For example, conversion of sound waves into nerve impulses is a very complicated process, yet the human ear has no trouble performing it.
“Electronic circuits that use these complex biological components could become much more efficient,” said Aleksandr Noy, the LLNL lead scientist on the project.
While earlier research has attempted to integrate biological systems with microelectronics, none have gotten to the point of seamless material-level incorporation.
“But with the creation of even smaller nanomaterials that are comparable to the size of biological molecules, we can integrate the systems at an even more localized level,” Noy said.
To create the bionanoelectronic platform the LLNL team turned to lipid membranes, which are ubiquitous in biological cells. These membranes form a stable, self-healing,and virtually impenetrable barrier to ions and small molecules.
“That's not to mention that these lipid membranes also can house an unlimited number of protein machines that perform a large number of critical recognition, transport and signal transduction functions in the cell,” said Nipun Misra, a UC Berkeley graduate student and a co-author on the paper.
Julio Martinez, a UC Davis graduate student and another co-author added: “Besides some preliminary work, using lipid membranes in nanoelectronic devices remains virtually untapped.”
The researchers incorporated lipid bilayer membranes into silicon nanowire transistors by covering the nanowire with a continuous lipid bilayer shell that forms a barrier between the nanowire surface and solution species.
“This 'shielded wire' configuration allows us to use membrane pores as the only pathway for the ions to reach the nanowire,” Noy said. “This is how we can use the nanowire device to monitor specific transport and also to control the membrane protein.”
The team showed that by changing the gate voltage of the device, they can open and close the membrane pore electronically.
The research appears Aug. 10 in the online version of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.